In the journey of learning music theory, one concept that you can quickly embrace is the idea of Roman numeral chords. You’ve probably seen these notations, like IV or V, interspersed in the sheet music and wondered about their significance.
These are not cryptic symbols to confuse you but rather tools designed to simplify your life. Roman numeral chords consist of an easy-to-navigate system that encodes chord progression information into your music.
It’s a silver bullet, illuminating the harmonic patterns and structural framework birthed by various scales and keys. The beauty of this system is that it transcends musical genres, outlining blues, and classical pieces to modern pop hits with equal flair.
What are Roman Numeral Chords?
Roman numeral chords, as per their name, represent chords using the Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV, etc.). By employing these symbols, music theorists can convey complex harmonic structures within varying musical contexts.
Circumventing the limitations of written key-specific chord names like C or F#, it delineates the fundamental structure of a piece’s interval relationship.
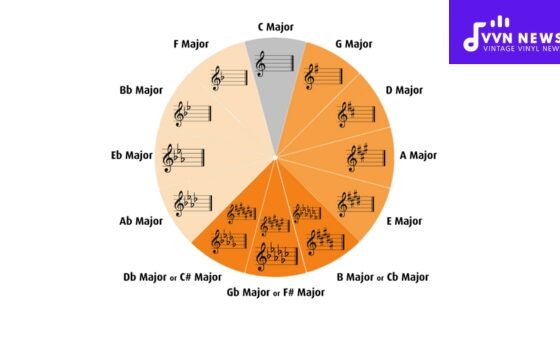
It conveys the relative position of each chord within a specific key. For instance, in the key of C Major: C is ‘I’, Dm is ‘II’, Em is ‘III’, and so forth. This system’s beauty is its flexibility – applicable across various keys without any alteration to the theoretical basis.
Also Read: Ear Training: Master Music Skills with Expert Techniques
What is the relationship of scales with Roman numeral chords?
Scales and Roman numeral chords work together as indispensable crossroads of melodies and harmonies in music.

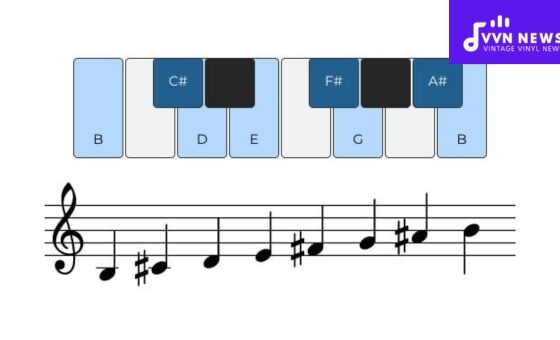
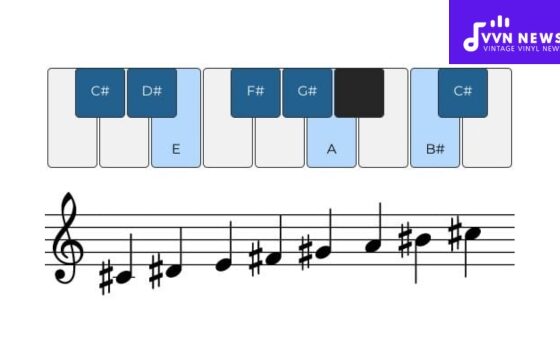
A musical scale is put simply as a series of notes organized by pitch, with the most common being the major and minor scales.
Now imagine assigning each note in a scale a Roman numeral. For example, in C major scale (C-D-E-F-G-A-B), C would be ‘I’, D ‘II’, E ‘III’, and so forth.
This way each numeral denotes a specific degree of the scale. Music often involves chords or combinations of multiple notes played simultaneously, giving rise to basic triads or three-note chords.
When you build a triad on each degree of your scale, this forms “Roman numeral chords”.
For instance, the chord progression I-IV-V represents playing triads built on the 1st (I), 4th (IV), and 5th (V) degrees of the given scales.
Consequently, irrespective of key changes or tonal differences, Roman numerals will remain constant designators for similar chord functions.
What are the different uses of Roman numeral chords?
The applications of Roman numeral chords are diverse, as they are deeply ingrained into the fabric of music.
These magical symbols can provide astounding clarity while you navigate complex musical terrain.
Transposition
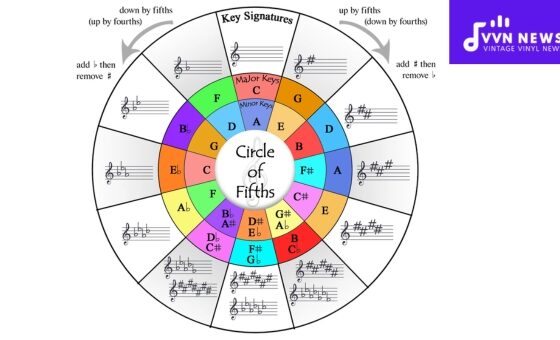
Transposing a song to a different key can often challenge your skills. When you approach this using Roman numerals, the task becomes remarkably simple.
For instance, if a sequence appears as I-IV-V in the key of C major (C-F-G), it will be the same in D major but with different notes (D-G-A).
Thus, Roman numeral chords act as conduits in interpreting patterns irrespective of keys.
Connecting Similar Harmonies
Roman numeral chord notation enables you to draw parallels between songs with similar harmonic changes.
They serve as a straightforward way to captivate how “Let It Be” by The Beatles and “No Woman No Cry” by Bob Marley possess rhythmically identical IV-I-V-V chord progression but in different keys.
Generating New Musical Concepts
A melody may seem simple, and yet it could hide fascinating combinations of Roman numeral chords.
Analyzing these structures could lead to discovering new musical concepts or inspiring innovative compositions.
Enhancing Communication
Roman numerals greatly streamline communication for musicians across the globe.
Band practices or studio jam sessions become more efficient due to these universally recognized annotations.
Roman numeral chords afford invaluable theoretical insights but also act as potent practical tools for musicians wishing to stretch their creative horizons.
What is the role of ear training in identifying Roman Numeral Chords?
Arguably, one of the most crucial elements to recognizing Roman numeral chords is ear training. It plays such a pivotal role, and here’s why:

- Enhances Perception: Through ear training, you can heighten your senses for different pitches and melodies. In turn, it becomes easier to discern chord characteristics and distinguish between the various Roman numeral chords.
- Builds Sound Recognition: As you develop strong auditory knowledge, differentiating particular chord progressions becomes significantly easier. It’s like learning a new language – once your ears are familiar with the sounds, you can recognize their patterns and implications.
- Increases Musical Versatility: Equipped with ear training as an asset, you’re not limited to sheet music or memorized songs anymore – you can actively participate in improvisations or jamming sessions as well! You’ll be able to comprehend the chord progression simply by listening.
- Empowers Songwriting Efforts: Composing music becomes a breeze when your ears can pick up chord sequences easily. You can identify certain chord progressions that stir certain feelings and then apply them in your compositions for a moody or uplifting feel – whatever it is that your song needs!
- Nurtures A Deeper Connection With Music: The more proficiently you’re able to identify chords by listening alone, the deeper your bond grows with the music itself. You start experiencing music beyond just entertainment – it becomes an extension of self-expression.
Ear training sets a solid foundation in mastering Roman numeral chord recognition; it opens up possibilities within yourself as an artist that is too exciting not to explore.
Also Read: How To Keep Christmas Music Lessons Fun Online? [Easy Tips]
How Roman numeral chords can be used to identify seventh chords and inversions?
Seventh chords and inversions play a considerable role in imparting depth and complexity to music, with Roman numeral chords facilitating their comprehension.
Recognizing Chords
The foremost step towards efficacious identification includes getting acquainted with basic seventh chords–– major, minor, dominant, and diminished.
- Major Seventh Chords are represented as IMaj7, IVMaj7 with upper case numerals followed by ‘Maj7’. For instance, in the key of C, IMaj7 would indicate CMaj7.
- Minor Seventh Chords (ii7) are notated with lowercase numerals succeeded by ‘7’. In the key of C, ii7 would symbolize Dmin7.
- A Dominant Seventh chord (V7) generally uses uppercase numerals suffixed by ‘7’, where V7 in the key of C represents G7.
The much elusive Diminished Seventh chord° is typically vii°. It comprises lowercase numerics crowned with a diminutive degree circle. A vii° in the key of C personifies Bdim°.
Recognizing Inversions:
Identifying inversions becomes effortless once you’ve mastered basic chord structures.
An inversion merely rearranges chord notes bringing a non-root note to the forefront.
Roman numeral chords use alphabets (a/b/c) or figures for mapping these scenarios:
- A first inversion (notated as /b or 6/3) involves shifting the third note of a chord onto the bass (bottom).
- A second inversion (/c or 6/4) promotes the fifth note to bass.
- A third inversion is exclusive to seventh chords (/d or 4/2) and transposes the seventh note into bass position.
This comprehensive tool makes identifying complex music notations much easier – whether you’re reading sheet music or trying to identify the harmonic pattern of your favorite song by ear.
Also Read: F Sharp Major Triad [Enhance Your Musical Compositions]
FAQs
What do Roman numeral chords signify in music theory?
Roman numerals in music theory label the chords that are built on the degrees of a key scale, making transposing easier.
How can I determine the quality of a chord from its Roman numeral?
Uppercase numerals (I, IV, V) typically denote major chords, while lowercase numerals (ii, iii, vi) indicate minor chords.
Can Roman numeral analysis be applied to any musical genre?
Yes, Roman numeral analysis is versatile and can be used across genres from classical to contemporary styles.
Is it necessary to learn Roman numeral chords to write music?
While not mandatory, Roman numeral chords is highly beneficial for composing and analyzing music harmonically.
Do Roman numerals relate to specific keys or notes?
Roman numerals relate to scale degrees rather than specific keys or notes, making the system universally applicable.
Also Read: How To Transpose Into The Tenor Clef? [Mastering In Notation]
Conclusion
Roman numeral chords offer a dynamic gateway to musical structures and progressions across any key. Their versatility makes them invaluable for composers, performers, and students alike.
By mastering this notation, you empower yourself to recognize patterns, modulate seamlessly between keys, and ultimately enhance your musical expression.
To harness this knowledge effectively, practice regularly and immerse yourself in diverse musical genres.